一. Spark SQL概述
什么是Spark SQL
Spark SQL是Spark用来处理结构化数据的一个模块,它提供了一个编程抽象叫做DataFrame并且作为分布式SQL查询引擎的作用
Spark SQL特点
-
Integrated Seamlessly mix SQL queries with Spark program
-
Uniform Data Access Connect to any data source the same way
-
Hive Compatibility Run unmodified Hive queries on existing data
-
Standard Connectivity Connect through JDBC or ODBC
二. DataFrames
什么是DataFrames
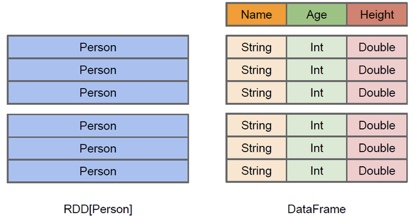
与RDD类似,DataFrame也是一个分布式数据容器,然而DataFrame更像传统数据库的二维表格,除了数据外,还记录数据的结构信息,即schema。同时,与Hive类似,DataFrame也支持嵌套数据类型(struct、array和map)。从API易用性的角度上 看,DataFrame API提供的是一套高层的关系操作,比函数式的RDD API要更加友好,门槛更低。由于与R和Pandas的DataFrame类似,Spark DataFrame很好地继承了传统单机数据分析的开发体
创建DataFrames
在Spark SQL中SQLContext是创建DataFrames和执行SQL的入口,在spark-1.5.2中已经内置了一个sqlContex
- 在本地创建一个文件,有三列,分别是id、name、age,用空格分隔,然后上传到hdfs上
# vi person.txt 1,laozhao,18 2,laoduan,30 3,laomao,28 hdfs dfs -put person.txt / - 在spark shell执行下面命令,读取数据,将每一行的数据使用列分隔符分割
val rdd = sc.textFile("hdfs://hadoop1:8020/person.txt").map(_.split(",")) - 定义case class(相当于表的schema)
case class Person(id: Long, name: String, age: Int) - 将RDD和case class关联
val personRDD = rdd.map(x => Person(x(0).toLong, x(1), x(2).toInt)) - 将RDD转换成DataFrame
val personDF = personRDD.toDF - 对DataFrame进行处理
personDF.show personDF.select("id", "name").show
三. DataFrame常用操作
DSL风格语法
- 查看DataFrame中的内容
personDF.show - 查看DataFrame部分列中的内容
personDF.select(personDF.col("name")).show personDF.select(col("name"), col("age")).show personDF.select("name").show - 打印DataFrame的Schema信息
personDF.printSchema - 查询所有的name和age,并将age+1
personDF.select(col("id"), col("name"), col("age") + 1).show personDF.select(personDF("id"), personDF("name"), personDF("age") + 1).show - 过滤age大于等于18的
personDF.filter(col("age") >= 18).show - 按年龄进行分组并统计相同年龄的人数
personDF.groupBy("age").count().show()
SQL风格语法
如果想使用SQL风格的语法,需要将DataFrame注册成表
personDF.registerTempTable("t_person")
- 查询年龄最大的前两名
sqlContext.sql("select * from t_person order by age desc limit 2").show - 显示表的Schema信息
sqlContext.sql("desc t_person").show
四. 以编程方式执行Spark SQL查询
通过反射推断Schema
case class Person(id: Long, name: String, age: Int)
object InferringSchema {
def main(args: Array[String]) = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("InferringSchema")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val lineRDD = sc.textFile("person.txt").map(_.split(","))
val personRDD = lineRDD.map(x => Person(x(0).toLong, x(1), x(2).toInt))
// 导入隐式转换,将rdd转换为DataFrame
import sqlContext.implicits._
val personDF = personRDD.toDF
// 注册表
personDF.registerTempTable("t_person")
// 传入SQL
val df = sqlContext.sql("select * from t_person order by age desc limit 2")
// 将结果以JSON的方式存储到指定位置
df.write.json("person.json")
sc.stop()
}
}
通过StructType直接指定Schema
object SpecifyingSchema {
def main(args: Array[String]) = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("InferringSchema")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val lineRDD = sc.textFile("person.txt").map(_.split(","))
// 通过StructType直接指定每个字段的schema
val schema = StructType(List(
StructField("id", LongType, true),
StructField("name", StringType, true),
StructField("age", IntegerType, true)
))
// 将lineRDD映射到rowRDD
val rowRDD = lineRDD.map(p => Row(p(0).toLong, p(1), p(2).toInt))
// 将schema信息应用到rowRDD上
val personDF = sqlContext.createDataFrame(rowRDD, schema)
// 注册表
personDF.registerTempTable("t_person")
// 传入SQL
val df = sqlContext.sql("select * from t_person order by age desc limit 2")
// 将结果以JSON的方式存储到指定位置
df.write.json("/tmp/person")
sc.stop()
}
}
五. 从不同的数据源加载数据
JSON
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
val df = sqlContext.read.json("src/json")
df.registerTempTable("jtable")
val result = sqlContext.sql("select * from jtable")
result.show()
MySQL
val conf = new SparkConf().setMaster("local[*]").setAppName("CreateDFFromMysql2")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val sqlContext = new SQLContext(sc)
// 连接mysql需要的配置信息
val options = new mutable.HashMap[String, String]()
options.put("url", "jdbc:mysql://10.211.55.7:3306/spark")
options.put("driver", "com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
options.put("user", "root")
options.put("password", "MyNewPass4!")
options.put("dbtable", "person")
// 读取mysql数据库创建DataFrame
val person: DataFrame = sqlContext.read.format("jdbc").options(options).load()
person.show()
person.registerTempTable("t_person")
// 查询表
val result: DataFrame = sqlContext.sql("select * from t_person where t_person.age > 18")
// 结果存放到mysql
val properties: Properties = new Properties
properties.setProperty("user", "root")
properties.setProperty("password", "MyNewPass4!")
result.write.mode(SaveMode.ErrorIfExists).jdbc("jdbc:mysql://10.211.55.7:3306/spark", "query_result", properties)
sc.stop()