一. shuffle阶段执行过程
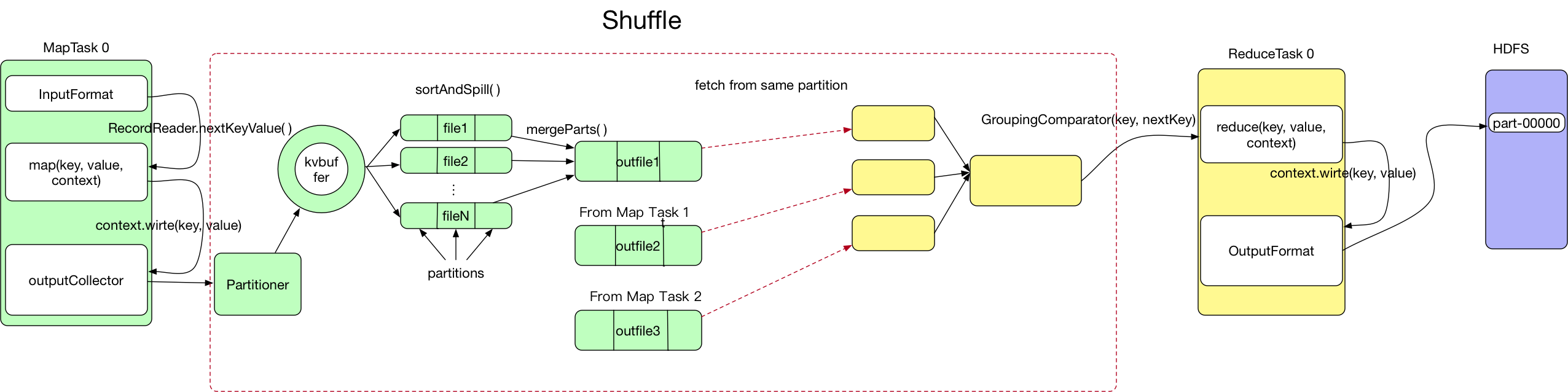
- shuffle是MapReduce处理流程中的一个过程,大致分为如下过程
- maptask收集map方法输出的k,v对,放入内存缓冲区中
- 在内存缓冲区中不断溢出本地磁盘文件
- 多个溢出的文件会被合并成大的溢出文件
- 在溢出过程中,及合并的过程中,都要调用partitioner进行分组和针对key进行排序
- reducetask根据自己的分区号,去各个maptask机器上取相应的分区数据
- reducetask会将取到的同一分区的来自不同maptask的结果文件进行合并
- 合并成大文件后,shuffle阶段结束。
二. shuffle阶段源码分析
- MapOutputCollector
用户自定义的Mapper类的map方法中调用context.write(key, value)来将结果进行输出,context.write会调用NewOutputCollector的write方法
public void write(K key, V value) throws IOException, InterruptedException { // collector默认为MapOutputBuffer collector.collect(key, value, partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions)); }collector会在NewOutputCollector构造方法中通过createSortingCollector方法获得,如果没有手动设置,默认为MapOutputBuffer
- 首先先看MapOutputBuffer的init方法(因为长度原因,省略了部分不涉及数据逻辑的代码)
public void init(MapOutputCollector.Context context ) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException { // 获取reduce个数,客户端中通过job.setNumReduceTasks()设置 // 如果不设置默认为1 partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks(); //sanity checks // 默认当缓冲区占用容量至80%时进行溢写,也是可以优化的地方 final float spillper = job.getFloat(JobContext.MAP_SORT_SPILL_PERCENT, (float)0.8); // 默认缓冲区大小为100mb,为了提升性能,可以调高 final int sortmb = job.getInt(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB, 100); indexCacheMemoryLimit = job.getInt(JobContext.INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT, INDEX_CACHE_MEMORY_LIMIT_DEFAULT); // sort的时候默认为快速排序 sorter = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(job.getClass("map.sort.class", QuickSort.class, IndexedSorter.class), job); // buffers and accounting // 默认值为104857600,<< 20相当于 sortmb * (2^20),表示需要104857600bytes的内存 int maxMemUsage = sortmb << 20; // METASIZE的值为16, NMETA = 4表示num meta ints, METASIZE = NMETA * 4 // 表示size in bytes // 这里减去maxMemUsage % METASIZE是为了使得maxMemUsage刚好是METASIZE的整数倍 maxMemUsage -= maxMemUsage % METASIZE; // 100mb大小的数组,用作数据存放缓冲区 kvbuffer = new byte[maxMemUsage]; // bufvoid : marks the point where we should stop reading at the end of the buffer bufvoid = kvbuffer.length; // kvmeta : metadata overlay on backing store // kvmeta是NIO的IntBuffer对象,表示在kvbuffer中存放索引数据的区域 kvmeta = ByteBuffer.wrap(kvbuffer) .order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder()) .asIntBuffer(); setEquator(0); // bufindex是指向kvbuffer写数据的位置指针 bufstart = bufend = bufindex = equator; // kvindex是指向kvmeta写索引的位置指针 kvstart = kvend = kvindex; maxRec = kvmeta.capacity() / NMETA; // 当缓冲区数据达到softLimit时开始溢写, 默认为 softLimit = (int)(kvbuffer.length * spillper); // bufferRemaining表示再写入多少数据时,才会发生溢写 bufferRemaining = softLimit; LOG.info(JobContext.IO_SORT_MB + ": " + sortmb); LOG.info("soft limit at " + softLimit); LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufvoid = " + bufvoid); LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "; length = " + maxRec); // k/v serialization // key比较器,map溢写结果在分区内有序 // 如果key为自定义的类,这个类实现WritableComparable后 // 这里得到的comparator将会是getMapOutputKeyClass().asSubclass(WritableComparable.class) comparator = job.getOutputKeyComparator(); // 获得客户端中设置的输出key类型 job.setMapOutputKeyClass(...) keyClass = (Class<K>)job.getMapOutputKeyClass(); // 获得客户端中设置的输出value类型 job.setMapOutputValueClass(...) valClass = (Class<V>)job.getMapOutputValueClass(); // 从配置文件读取序列化类的集合 serializationFactory = new SerializationFactory(job); keySerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(keyClass); // 打开BlockingBuffer流,也就是后面输出key,value时会往这个BlockingBuffer // 流中写内容,BlockingBuffer内部封装了一个Buffer keySerializer.open(bb); valSerializer = serializationFactory.getSerializer(valClass); valSerializer.open(bb); // compression // 检查是否设置了压缩编码 if (job.getCompressMapOutput()) { Class<? extends CompressionCodec> codecClass = job.getMapOutputCompressorClass(DefaultCodec.class); codec = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(codecClass, job); } else { codec = null; } // combiner final Counters.Counter combineInputCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_INPUT_RECORDS); // 获得用户设置的CombinerClass,如何没有设置,默认为null combinerRunner = CombinerRunner.create(job, getTaskID(), combineInputCounter, reporter, null); if (combinerRunner != null) { final Counters.Counter combineOutputCounter = reporter.getCounter(TaskCounter.COMBINE_OUTPUT_RECORDS); combineCollector= new CombineOutputCollector<K,V>(combineOutputCounter, reporter, job); } else { combineCollector = null; } spillInProgress = false; minSpillsForCombine = job.getInt(JobContext.MAP_COMBINE_MIN_SPILLS, 3); spillThread.setDaemon(true); spillThread.setName("SpillThread"); spillLock.lock(); try { // 数据的溢写是由另一个线程完成的 // 这样可以使得数据边写入缓冲区的时候边溢写,提高效率 spillThread.start(); while (!spillThreadRunning) { spillDone.await(); } } catch (InterruptedException e) { throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", e); } finally { spillLock.unlock(); } if (sortSpillException != null) { throw new IOException("Spill thread failed to initialize", sortSpillException); } }init方法中初始化接下来完成溢写工作需要的类,并启动了Spill线程。
- 接着看下MapOutputBuffer中的collect方法。
public synchronized void collect(K key, V value, final int partition ) throws IOException { // bufferRemaining表示再写入多少数据时,才会发生溢写 bufferRemaining -= METASIZE; // 当bufferRemaining <= 0时,开启溢写 if (bufferRemaining <= 0) { // start spill if the thread is not running and the soft limit has been // reached spillLock.lock(); try { do { if (!spillInProgress) { ... // startSpill设置信号量,使SpillThread调用sortAndSpill方法对 // 缓存中的数据进行排序后溢写出文件 startSpill(); .... } } while (false); } finally { spillLock.unlock(); } } try { // serialize key bytes into buffer int keystart = bufindex; keySerializer.serialize(key); if (bufindex < keystart) { // wrapped the key; must make contiguous bb.shiftBufferedKey(); keystart = 0; } // serialize value bytes into buffer final int valstart = bufindex; // 如果value是Text类型的,内部的调用链如下 // WritableSerialize()方法中调用w.write()方法,w.write()调用的是Text的write方法 // Text的write方法中调用的是MapOutoutBuffer内部类Buffer的write方法,在Buffer的write // 方法中完成数据写入缓冲区(kvbuff)的过程 valSerializer.serialize(value); bb.write(b0, 0, 0); // the record must be marked after the preceding write, as the metadata // for this record are not yet written int valend = bb.markRecord(); mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1); mapOutputByteCounter.increment( distanceTo(keystart, valend, bufvoid)); // write accounting info // 第一个参数表示的是offset,第二个参数是要写入的数据 // 存放分区号,kvindex+xxx表示的是内存中的地址 kvmeta.put(kvindex + PARTITION, partition); // 存放key起始位置 kvmeta.put(kvindex + KEYSTART, keystart); // 存放value起始位置 kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALSTART, valstart); // 存放value的长度 kvmeta.put(kvindex + VALLEN, distanceTo(valstart, valend)); // advance kvindex // 索引增长方式向下 // kvmeta.capacity()为缓冲区的大小/4 (因为一个kvmeta需要占用4个字节) kvindex = (kvindex - NMETA + kvmeta.capacity()) % kvmeta.capacity(); } catch (MapBufferTooSmallException e) { LOG.info("Record too large for in-memory buffer: " + e.getMessage()); spillSingleRecord(key, value, partition); mapOutputRecordCounter.increment(1); return; } } - Serializer.serialize中调用的向kvbuffer写k,v数据的write方法
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException { // 缓冲区大小占80%时开启SpillThread溢写 bufferRemaining -= len; if (bufferRemaining <= 0) { spillLock.lock(); try { do { .... } while (blockwrite); } finally { spillLock.unlock(); } } // here, we know that we have sufficient space to write // bufvoid定义是 kvbuffer.length; // 这步处理的是如果要写的数据大小加上已经有的数据大小,超过kvbuffer的大小 // 需要处理的逻辑 if (bufindex + len > bufvoid) { final int gaplen = bufvoid - bufindex; System.arraycopy(b, off, kvbuffer, bufindex, gaplen); len -= gaplen; off += gaplen; bufindex = 0; } // arraycopy会把序列化后的数据b,写入kvbuffer中 System.arraycopy(b, off, kvbuffer, bufindex, len); bufindex += len; }Kvbuffer,名如其义,但是这里面不光放置了数据,还放置了一些索引数据,给放置索引数据的区域起了一个Kvmeta的别名,在Kvbuffer的一块区域上穿了一个IntBuffer(字节序采用的是平台自身的字节序)的马甲。数据区域和索引数据区域在Kvbuffer中是相邻不重叠的两个区域,用一个分界点来划分两者,分界点不是亘古不变的,而是每次Spill之后都会更新一次。初始的分界点是0,数据的存储方向是向上增长,索引数据的存储方向是向下增长,如图所示:
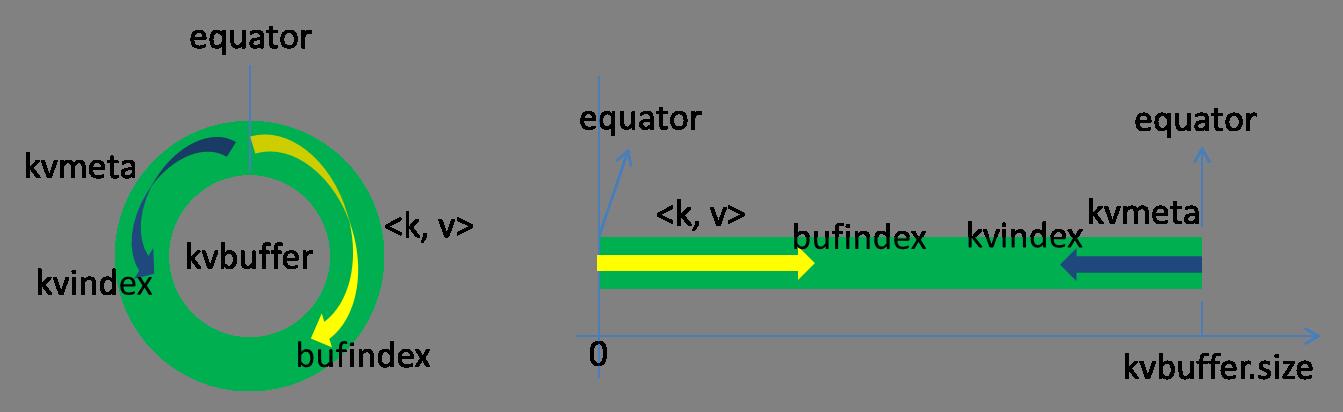 Kvbuffer的存放指针bufindex是一直闷着头地向上增长,比如bufindex初始值为0,一个Int型的key写完之后,bufindex增长为4,一个Int型的value写完之后,bufindex增长为8。
Kvbuffer的存放指针bufindex是一直闷着头地向上增长,比如bufindex初始值为0,一个Int型的key写完之后,bufindex增长为4,一个Int型的value写完之后,bufindex增长为8。
索引是对在kvbuffer中的键值对的索引,是个四元组,包括:value的起始位置、key的起始位置、partition值、value的长度,占用四个Int长度,Kvmeta的存放指针Kvindex每次都是向下跳四个“格子”,然后再向上一个格子一个格子地填充四元组的数据。比如Kvindex初始位置是-4,当第一个键值对写完之后,(Kvindex+0)的位置存放value的起始位置、(Kvindex+1)的位置存放key的起始位置、(Kvindex+2)的位置存放partition的值、(Kvindex+3)的位置存放value的长度,然后Kvindex跳到-8位置,等第二个键值对和索引写完之后,Kvindex跳到-12位置。
- 前面描述了k,v数据和其索引是如何通过collect方法写入kvbuffer中的,当数据达到spillper时(默认为80%)会向SpillThread发送信号,使得SpillThread启动SortAndSpill方法将排序并溢写至文件。这里为了观察方便,用{value}代表debug调试时获得的变量值。
private void sortAndSpill() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { //approximate the length of the output file to be the length of the //buffer + header lengths for the partitions // 预估的文件大小 {size : 2044} final long size = distanceTo(bufstart, bufend, bufvoid) + partitions * APPROX_HEADER_LENGTH; FSDataOutputStream out = null; try { // create spill file // partitions = job.getNumReduceTasks() 分区的个数 {paritions : 10} final SpillRecord spillRec = new SpillRecord(partitions); // 溢写出文件的路径及文件名 // {filename : /tmp/hadoop-spencer/mapred/local/localRunner/root/jobcache/job_local2001897110_0001/attempt_local2001897110_0001_m_000000_0/output/spill0.out} final Path filename = mapOutputFile.getSpillFileForWrite(numSpills, size); // FSDataOutputStream打开文件,获取输出流 out = rfs.create(filename); final int mstart = kvend / NMETA; final int mend = 1 + // kvend is a valid record (kvstart >= kvend ? kvstart : kvmeta.capacity() + kvstart) / NMETA; // 将kvbuffer中的数据按照partiton值和key值升序排序 // 移动的只是索引数据 // {sorter : QuickSort} sorter.sort(MapOutputBuffer.this, mstart, mend, reporter); int spindex = mstart; final IndexRecord rec = new IndexRecord(); final InMemValBytes value = new InMemValBytes(); for (int i = 0; i < partitions; ++i) { IFile.Writer<K, V> writer = null; try { long segmentStart = out.getPos(); FSDataOutputStream partitionOut = CryptoUtils.wrapIfNecessary(job, out); writer = new Writer<K, V>(job, partitionOut, keyClass, valClass, codec, spilledRecordsCounter); // 检查是否设置了Combiner,MR中没有设置的话则为null if (combinerRunner == null) { // spill directly DataInputBuffer key = new DataInputBuffer(); // 将kvmeta中记录的分区号为i的数据写出 while (spindex < mend && kvmeta.get(offsetFor(spindex % maxRec) + PARTITION) == i) { final int kvoff = offsetFor(spindex % maxRec); int keystart = kvmeta.get(kvoff + KEYSTART); int valstart = kvmeta.get(kvoff + VALSTART); key.reset(kvbuffer, keystart, valstart - keystart); getVBytesForOffset(kvoff, value); // 向filename文件中写入数据 writer.append(key, value); ++spindex; } } else { int spstart = spindex; while (spindex < mend && kvmeta.get(offsetFor(spindex % maxRec) + PARTITION) == i) { ++spindex; } // Note: we would like to avoid the combiner if we've fewer // than some threshold of records for a partition if (spstart != spindex) { combineCollector.setWriter(writer); // 如果设置了Combiner则会将数据组成K, IterV的形式作为Combiner的输入 RawKeyValueIterator kvIter = new MRResultIterator(spstart, spindex); // 启动combiner combinerRunner.combine(kvIter, combineCollector); } } // close the writer writer.close(); // record offsets // 给SpillRecord复制 rec.startOffset = segmentStart; rec.rawLength = writer.getRawLength() + CryptoUtils.cryptoPadding(job); rec.partLength = writer.getCompressedLength() + CryptoUtils.cryptoPadding(job); spillRec.putIndex(rec, i); writer = null; } finally { if (null != writer) writer.close(); } } // 索引文件的缓冲区大小默认为1048576bytes,超过这个大小会写入磁盘中 if (totalIndexCacheMemory >= indexCacheMemoryLimit) { // create spill index file Path indexFilename = mapOutputFile.getSpillIndexFileForWrite(numSpills, partitions * MAP_OUTPUT_INDEX_RECORD_LENGTH); spillRec.writeToFile(indexFilename, job); } else { indexCacheList.add(spillRec); totalIndexCacheMemory += spillRec.size() * MAP_OUTPUT_INDEX_RECORD_LENGTH; } LOG.info("Finished spill " + numSpills); ++numSpills; } finally { if (out != null) out.close(); } }整个过程主要完成了两步,一是将MapOutPutBuffer中的kvbuffer进行排序(只是对kvmeta中的索引排序),其compare方法中先比较parition,partition相同再比较key。二是将k,v数据写入filename文件中去。
至此,从用户自定义的map方法中context.write输出k,v到k,v如何写入磁盘的过程已经大致写出。当map读取所有输入并且完成输出后,会关闭OutputCollector,out.close方法中会调用MapOutputBuffer的flush方法。在flush方法中会将kvbuffer中的数据溢写出,然后合并所有生成的溢写文件。(spill.1.out spill.2.out… => file.out)
public void flush() throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException,
InterruptedException {
LOG.info("Starting flush of map output");
spillLock.lock();
try {
while (spillInProgress) {
reporter.progress();
spillDone.await();
}
checkSpillException();
final int kvbend = 4 * kvend;
if ((kvbend + METASIZE) % kvbuffer.length !=
equator - (equator % METASIZE)) {
// spill finished
resetSpill();
}
if (kvindex != kvend) {
kvend = (kvindex + NMETA) % kvmeta.capacity();
bufend = bufmark;
LOG.info("Spilling map output");
LOG.info("bufstart = " + bufstart + "; bufend = " + bufmark +
"; bufvoid = " + bufvoid);
LOG.info("kvstart = " + kvstart + "(" + (kvstart * 4) +
"); kvend = " + kvend + "(" + (kvend * 4) +
"); length = " + (distanceTo(kvend, kvstart,
kvmeta.capacity()) + 1) + "/" + maxRec);
sortAndSpill();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Interrupted while waiting for the writer", e);
} finally {
spillLock.unlock();
}
assert !spillLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// shut down spill thread and wait for it to exit. Since the preceding
// ensures that it is finished with its work (and sortAndSpill did not
// throw), we elect to use an interrupt instead of setting a flag.
// Spilling simultaneously from this thread while the spill thread
// finishes its work might be both a useful way to extend this and also
// sufficient motivation for the latter approach.
try {
spillThread.interrupt();
spillThread.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new IOException("Spill failed", e);
}
// release sort buffer before the merge
kvbuffer = null;
mergeParts();
Path outputPath = mapOutputFile.getOutputFile();
fileOutputByteCounter.increment(rfs.getFileStatus(outputPath).getLen());
}
后面reduce端拉取结果,进行合并的过程逻辑上和之前差不多,等过段时间不忙了再分析吧。