一. MapTask执行图
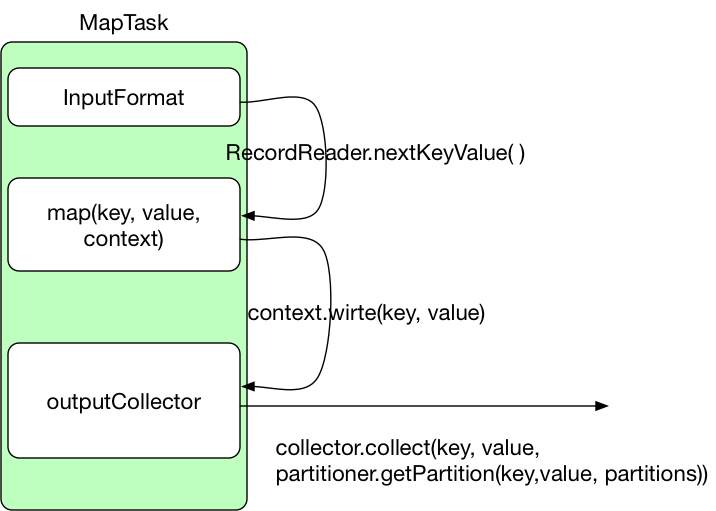 MapTask完成的任务大致如下:
MapTask完成的任务大致如下:
- 利用客户指定的inputformat来获取RecordReader读取数据,形成输入KV对
- 将输入KV对传递给客户定义的map()方法,做逻辑运算,并将map()方法输出的KV对收集到缓存
- 将缓存中的KV对按照K分区排序后不断溢写到磁盘文件
二. MapTask源码分析
- MapTask的run方法是执行map任务的入口,关于MapTask是如何被执行的可以看上一篇博客
public void run(final JobConf job, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { // TaskUmbilicalProtocal是子进程和父进程进行通信的协议 this.umbilical = umbilical; if (isMapTask()) { // If there are no reducers then there won't be any sort. Hence the map // phase will govern the entire attempt's progress. if (conf.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) { mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 1.0f); } else { // If there are reducers then the entire attempt's progress will be // split between the map phase (67%) and the sort phase (33%). mapPhase = getProgress().addPhase("map", 0.667f); sortPhase = getProgress().addPhase("sort", 0.333f); } } Task.TaskReporter reporter = startReporter(umbilical); boolean useNewApi = job.getUseNewMapper(); initialize(job, getJobID(), reporter, useNewApi); // check if it is a cleanupJobTask if (jobCleanup) { runJobCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (jobSetup) { runJobSetupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } if (taskCleanup) { runTaskCleanupTask(umbilical, reporter); return; } // Job提交的阶段会设置使用新旧API,默认为NewAPI if (useNewApi) { runNewMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter); } else { runOldMapper(job, splitMetaInfo, umbilical, reporter); } done(umbilical, reporter); } - 进入runNewMapper中
void runNewMapper(final JobConf job, final JobSplit.TaskSplitIndex splitIndex, final TaskUmbilicalProtocol umbilical, Task.TaskReporter reporter ) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, InterruptedException { // make a task context so we can get the classes // 创建task任务的上下文 // 这里的job是根据file://xxx/local/localRunner/root/jobId/jobId.xml生成的配置文件(jobConf) org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskAttemptContext taskContext = new org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl(job,getTaskID(), reporter); // make a mapper // 根据生成的taskContext反射生成mapper对象 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE> mapper = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>)ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getMapperClass(), job); // make the input format // 如果没有用job.setInputFormatClass,默认为TextInputFormat org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE> inputFormat = (org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat<INKEY,INVALUE>) ReflectionUtils.newInstance(taskContext.getInputFormatClass(), job); // rebuild the input split // 获得文件切片信息 // split信息中包含 // file路径 file: {hdfs://hadoop1:8020/wordcount/input/LICENSE.txt} // 起始位置 start: 0 // 长度 length: 84853 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit split = null; split = getSplitDetails(new Path(splitIndex.getSplitLocation()), splitIndex.getStartOffset()); LOG.info("Processing split: " + split); // 创建RecordReader用来从split中读取数据,默认为LineRecordReader org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> input = new MapTask.NewTrackingRecordReader<INKEY,INVALUE> (split, inputFormat, reporter, taskContext); job.setBoolean(JobContext.SKIP_RECORDS, isSkipping()); org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.RecordWriter output = null; // get an output object // 输出类,调用context.write时会调用outputCollector的collect方法 if (job.getNumReduceTasks() == 0) { output = new MapTask.NewDirectOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); } else { output = new MapTask.NewOutputCollector(taskContext, job, umbilical, reporter); } org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.MapContext<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE> mapContext = new MapContextImpl<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>(job, getTaskID(), input, output, committer, reporter, split); // 创建上下文对象 org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper<INKEY,INVALUE,OUTKEY,OUTVALUE>.Context mapperContext = new WrappedMapper<INKEY, INVALUE, OUTKEY, OUTVALUE>().getMapContext( mapContext); try { input.initialize(split, mapperContext); // run方法中会调用自定义Mapper类的map方法 mapper.run(mapperContext); mapPhase.complete(); setPhase(TaskStatus.Phase.SORT); statusUpdate(umbilical); input.close(); input = null; // 关闭outputCollector,在flush中会做shuffle output.close(mapperContext); output = null; } finally { closeQuietly(input); closeQuietly(output, mapperContext); } }这段代码的核心功能,一是在mapper的run方法中调用了用户自定义Mapper类的map方法,完成数据转换。二是在output.close中会开启shuffle
- 追踪mapper的run方法
public void run(Mapper.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { setup(context); try { // 如果使用默认的inputFormat会调用LineRecordReader的nextKeyValue方法 while (context.nextKeyValue()) { map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); } } finally { cleanup(context); } } - 没有设置inputFormat的情况下,context.nextKeyValue调用的事LineRecordReader的nextKeyValue方法
public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException { if (key == null) { key = new LongWritable(); } // key设置为每一行对应的偏移量 key.set(pos); if (value == null) { value = new Text(); } int newSize = 0; // We always read one extra line, which lies outside the upper // split limit i.e. (end - 1) // 为了避免切片的时候 同一行被划分到2个split中,读取数据的时候会多读一行 while (getFilePosition() <= end || in.needAdditionalRecordAfterSplit()) { if (pos == 0) { newSize = skipUtfByteOrderMark(); } else { // value被设置为读取的一行字符串 newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, maxBytesToConsume(pos)); // pos移到下一行行首 pos += newSize; } // maxLineLength默认为Integer.MAX_VALUE,正常情况每次只读取一行便break if ((newSize == 0) || (newSize < maxLineLength)) { break; } // line too long. try again LOG.info("Skipped line of size " + newSize + " at pos " + (pos - newSize)); } if (newSize == 0) { key = null; value = null; return false; } else { return true; } } - pos是在LineRecordReader的initialize方法中被初始化的
public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException { ... start = split.getStart(); end = start + split.getLength(); final Path file = split.getPath(); ... // If this is not the first split, we always throw away first record // because we always (except the last split) read one extra line in // next() method. // 除了第一个split切片,其他的切片会舍弃第一行,读取下一个split的第一行 if (start != 0) { start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, maxBytesToConsume(start)); } this.pos = start; } - LineRecordReader的nextKeyValue每调用一次,便会执行一次自定义Mapper中的map方法,map方法中通过context.write(k, v)输出结果,context.write会调用MapOutputBuffer的collect方法(只要reduce个数不为0),
collector.collect(key, value, partitioner.getPartition(key, value, partitions))。 关于shuffle阶段执行的流程可以看下一篇博客